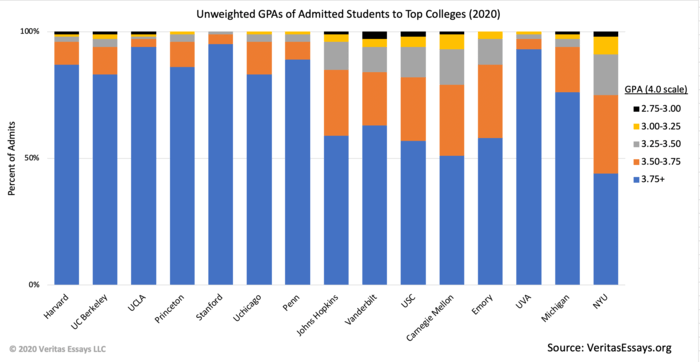
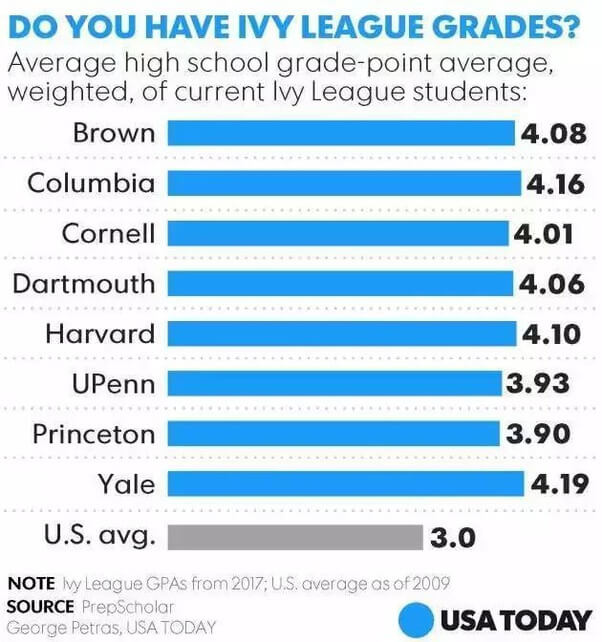
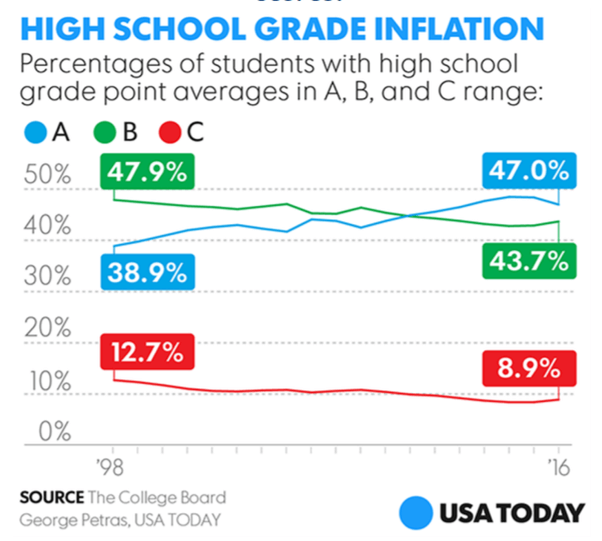
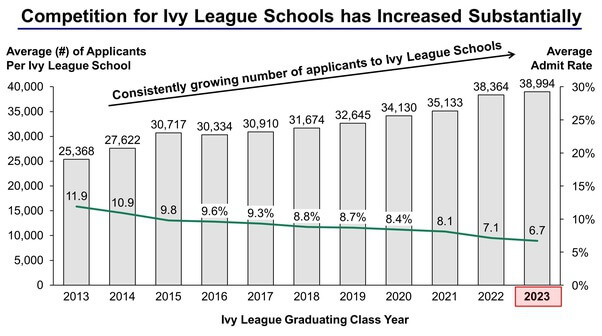
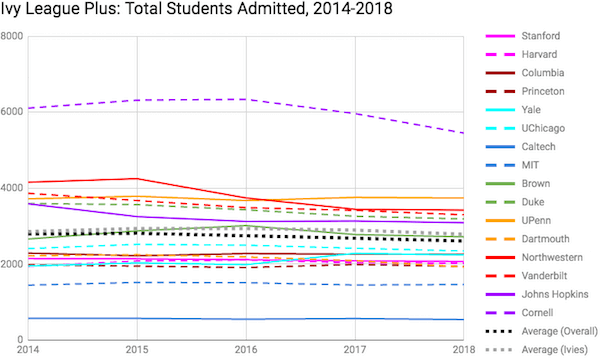
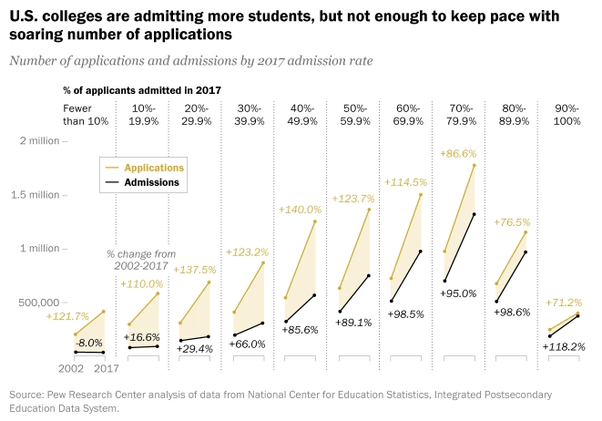
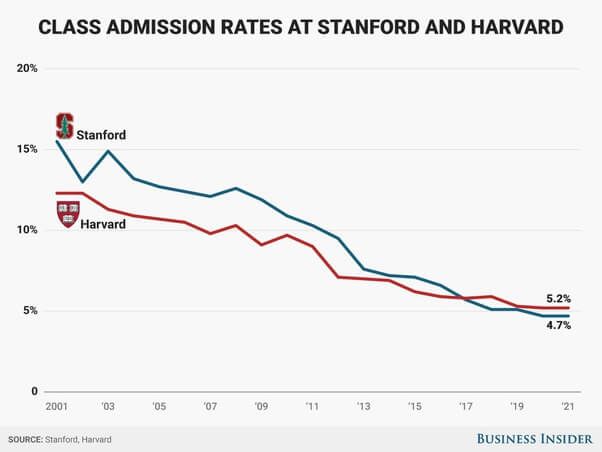
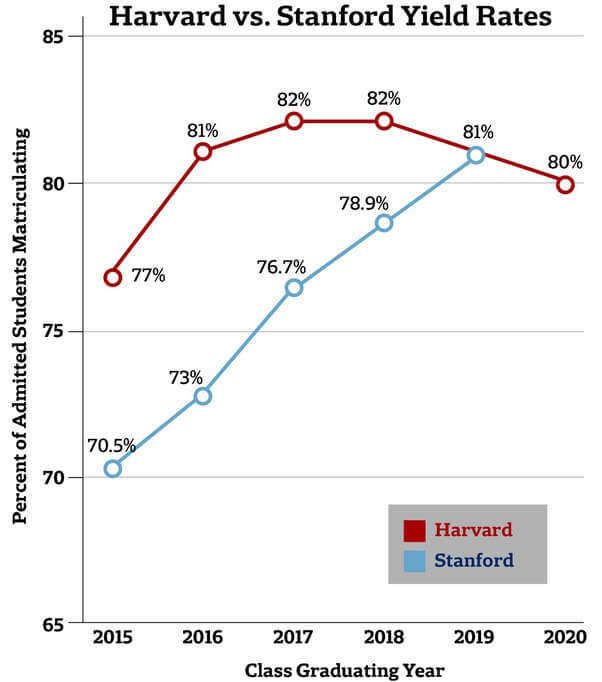
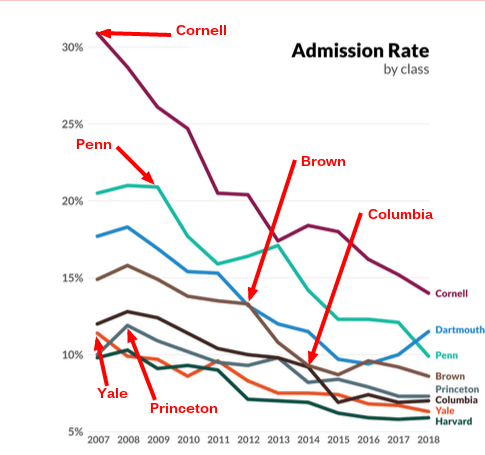
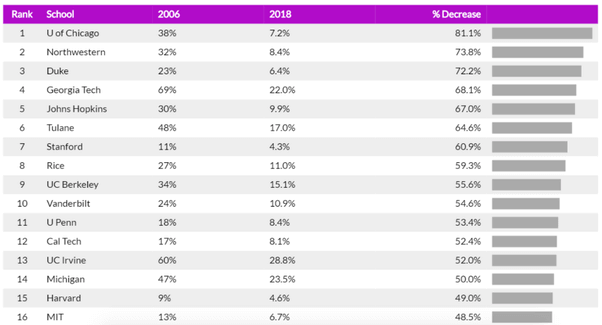
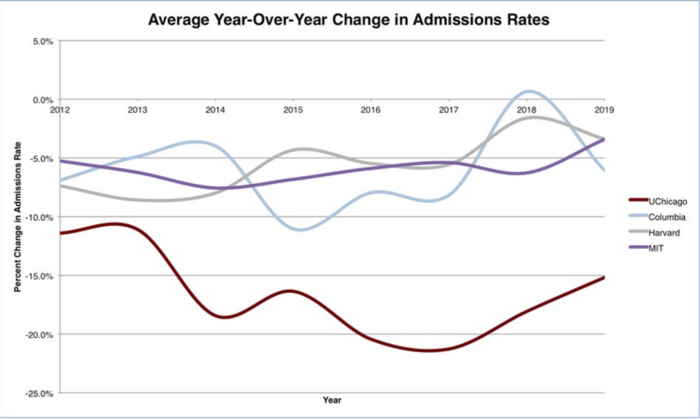
While each Ivy is unique, they share similarly high standards for accepting applicants and tend to draw from the same pool of exceptional individuals.
They are also incredibly secretive about their admissions practices.
Luckily, one of them -- Harvard -- was forced to reveal incredibly detailed information on its admissions practices through both a recent federal lawsuit as well as FERPA records requests submitted by our own Essay Mentors to view their admissions files.
Read on to learn the Ivy League admissions secrets behind getting into an Ivy League school, and use this information to better prepare your application to get into the Ivy League. (Note: No other Ivy League school has released such detailed information on its admissions practices, so this may be the best glimpse into what are likely common practices amongst Ivy League admissions offices)
Q: How are applicants selected?
A: First, they are graded on 4 dimensions using a scale of 1 (best) to 6 (worst) with +/-’s in between.
After taking into account background factors (legacy, donor status, minority, geographic location, etc.), the applicants with the best ratings are selected.
At Yale , on the other hand, they use a scale of 1 (best) to 4 (worst), but the principle is the same.

Q: How are ratings assigned to applicants?
A: The 4 dimensions on which all applicants are graded are:
- Academics
- Extracurriculars (“ECs”)
- Personal Qualities (“PQs”)
- Athletics
Each applicant is rated on a scale of 1 (best) to 6 (worst) across each dimension, with +/-’s for more nuanced ratings. The scale is interpreted as follows (image taken directly from Harvard’s Internal Admissions Handbook :
Q: What do admissions officers talk about during admissions office proceedings behind closed doors? How fast do admissions officers read applications?
Admissions officers read essays on their own time, then reconvene during admissions committee meetings to discuss applications and decide on admissions.
Admissions officers read applications incredibly fast, a skill sharpened by churning through 40,000+ applications. During a 2-hour committee session, a group of admissions officers will read and evaluate roughly 300 applications, then decide on accepting or rejecting each application.
As Yale Admissions Officer Ed Boland writes,
You could look down at the names of four or five kids from one school who were terribly smart but not exceptional and say, “Reject the entire high school”; sometimes you could go further and say, “Reject the page,” and send 20 kids on a single page of computer paper packing; or, most famously, “Reject the state,” when it came to sparsely populated places like North Dakota or Wyoming.
Q: What does my application look like to the admissions office?
A: For Harvard specifically, your admissions file will get boiled down into the following one-page summary sheet:
Q: How do I get the best rating in each category on which my application will be graded?
A: The answers, quoted directly from Harvard’s Admissions Handbook, are as follows.
Academics
- Summa potential. Genuine scholar; near-perfect scores and grades (in most cases) combined with unusual creativity and possible evidence of original scholarship.
- Magna potential: Excellent student with superb grades and mid-to high-700 scores (33+ ACT).
- Cum laude potential: Very good student with excellent grades and mid-600 to low-700 scores (29 to 32 ACT).
- Adequate preparation. Respectable grades and low-to mid-600 scores (26 to 29) ACT).
- Marginal potential. Modest grades and 500 scores (25 and below ACT).
- Achievement or motivation marginal or worse.
Extracurriculars
- Unusual strength in one or more areas. Possible national-level achievement or professional experience. A potential major contributor at Harvard. Truly unusual achievement.
- Strong secondary school contribution in one or more areas such as class president, newspaper editor, etc. Local or regional recognition; major accomplishment(s).
- Solid participation but without special distinction. (Upgrade 3+ to 2- in some cases if the e/c is particularly extensive and substantive.)
- Little or no participation.
- Substantial activity outside of conventional EC participation such as family commitments or term-time work (could be included with other e/c to boost the rating or left as a "5" if it is more representative of the student's commitment).
- Special circumstances limit or prevent participation (e.g. a physical condition).
Personal Qualities (Essays, Teacher Recs, School Rec, Interview)
- Outstanding
- Very strong
- Generally positive
- Bland or somewhat negative or immature
- Questionable personal qualities.
- Worrisome personal qualities
Athletics
- Unusually strong prospect for varsity sports at Harvard, desired by Harvard coaches.
- Strong secondary school contribution in one or more areas; possible leadership role(s).
- Active participation.
- Little or no interest.
- Substantial activity outside of conventional EC participation such as family commitments or term-time work (could be included with other e/c to boost the rating or left as a "5" if it is more representative of the student's commitment).
- Physical condition prevents significant activity.
Q: How are my academics (GPA, transcript, SAT score, ACT score, AP scores, etc.) weighed?
A: All of the Ivies use the Ivy League Academic Index (AI) to score applicants' academic aptitudes on a scale from 60-240. All applicants are graded on this AI.
The Academic Index was originally used by the Ivy League as a standardized metric for assessing the intellectual quality of each school's incoming class of athletic recruits.
The Ivy League colleges all compete in a sports league that is also referred to as the "Ivy League." In order to ensure that some Ivy League colleges don't "dumb down" their classes, and thus tarnish the intellectual reputation of the Ivy League, by recruiting students who excel at sports but aren't academically inclined, the Ivy League requires that all admitted athletic recruits have an AI above 170, and that the average AI of students on sports teams is within a standard deviation of the overall campus's average student AI.
The average AI of an incoming student is about 220 at Princeton, Yale, and Harvard.
The average Academic Index at Dartmouth, Brown, and Penn is about 215.
And the average Academic Index at Columbia and Cornell is about 210.
Q: How is the Ivy League Academic Index calculated?
There are 3 separate components to the Ivy League Academic Index, each of which is scored from 20-80.
- Class Rank Conversion: Takes your unweighted GPA and adjusts it to the reputation of your school/strength of your courseload.
If you are an international student and have taken IB tests and courses under the International Baccalaureate system, then then following conversion chart is used to convert your IB grades into an "American" GPA. Higher Level courses are given double the weight as Standard Level courses.
7 = A+ = 4.3
6 = A = 4.0
5 = B = 3.0
4 = C = 2.0
3 = D = 1.0
If you are an international student whose high school follows the British system for grading, then the following conversion chart is used to convert your British grades into "an American" GPA. A Level grades are weighed twice as heavily as AS and GCSE grades.
A* = 4.3
A = 4.0
B = 3.0
C = 2.0
D = 1.0
If you are an international student from Singapore , then the following conversion chart is used to convert your H3 grades into "an American" GPA.
Distinction = A = 4.0
Merit = B = 3.0
Pass = C = 2.0
If you are an international student from New Zealand , then the following conversion chart is used to convert your grades into "an American" GPA.
Excellent = A = 4.0
Merit = B = 3.0
Achieved = C = 2.0
Not Achieved = F = 0.0
So then how does the Ivy League calculate your GPA and convert it into a raw AI score?
The table below shows how to convert the most common grading scales (percentile scores, 6.0/7.0/11.0/12.0 grade scales, letter grades, etc.) into a raw AI Class Rank Conversion score (CGS):
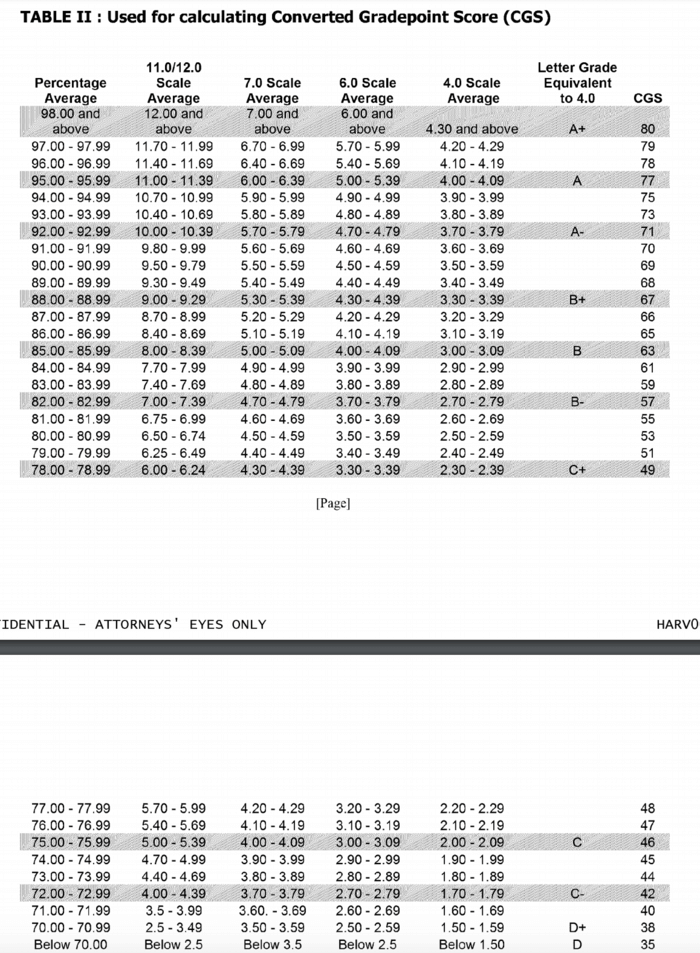
- SAT/ACT Scores: A perfect score on either the SAT or ACT will give you the maximum 80 points for this category.
- Best 2 SAT Subject Test Scores: If you get an 800/800 on two of the SAT Subject Tests that you report, then you'll receive a full 80 here.